به عنوان یک خریدار دریچه حرفه ای, you need to have enough comprehensive knowledge to make reasonable purchasing decisions.
The work of valve procurement can be systematically divided into the following five dimensions: technical performance, quality compliance, cost control, supply chain management, and full life cycle maintenance.
فهرست مطالب
تغییر وضعیت دهید1. Valve Types and Functions

1.1 Valve Types
- Valve type: شیر توپی/gate valve/stop valve/globe valve, etc.
First of all, you have to clarify the usage scenarios and requirements. The main functions of the valve are only three: open and close, adjust the flow, and prevent backflow. According to the different pipeline systems, different valves need to be chosen.
به عنوان مثال, ball valves are suitable for liquid and gas pipelines that need to be opened and closed quickly; gate valves are suitable for liquid, گاز, and steam pipelines that require flow conditions and do not need to be opened and closed frequently; and check valves are suitable for one-way flow pipes.
Defining the type of valve is the first step in purchasing a valve.
1.2 Basic Parameters of the Valve
- Nominal diameter DN: the nominal diameter of the valve should match the pipe; If the diameter of the front and back pipe segments is inconsistent, it is necessary to select the BUSHING joint (the junction of the main pipe and the branch pipe segment)
- DN15-DN25: common civilian
- DN125-DN50: Conventional industrial use
- DN80-DN150: Large industrial use
- DN200 and above: Large-scale water treatment facilities
| Valve DN Size and Inch Size Conversion Table | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMAG | ||||
| NPS (اینچ) |
DN (mm) |
NPS (اینچ) |
DN (mm) |
|
| 1/2″ | DN15 | 14″ | DN350 | |
| 3/4″ | DN20 | 16″ | DN400 | |
| 1″ | DN25 | 18″ | DN450 | |
| 1-1/4″ | DN32 | 20″ | DN500 | |
| 1-1/2″ | DN40 | 22″ | DN550 | |
| 2″ | DN50 | 24″ | DN600 | |
| 2-1/2″ | DN65 | 26″ | DN650 | |
| 3″ | DN80 | 28″ | DN700 | |
| 4″ | DN100 | 30″ | DN750 | |
| 5″ | DN125 | 32″ | DN800 | |
| 6″ | DN150 | 36″ | DN900 | |
| 8″ | DN200 | 40″ | DN1000 | |
| 10″ | DN250 | 44″ | DN1100 | |
| 12″ | DN300 | 48″ | DN1200 | |
1.3 Valve Connection Method
- flange connection valve
Flange connection By bolting two flange plates together to form a sealed joint, suitable for high pressure and high temperature environments. Usually can withstand high pressure (up to 25 MPa or more)

- threaded connection valve
Threaded connection Using the intermesh of threads to connect pipes or equipment, suitable for small diameter pipes and low pressure applications.
Threads according to different national standards are divided into: Metric Thread, Imperial Thread, NPT Thread (National Pipe Thread), BSP thread (British Standard Pipe), JIS thread (Japanese Industrial Standard), G Thread (Gas Thread), ACME thread
Usually suitable for low to moderate pressures (up to 16 MPa)

- butt welded connection valve
Butt welded joint by joining and welding the ends of two sections of pipe to form a strong connection, often used in high pressure and high temperature applications.
Can withstand high pressure (up to 50 MPa)

- clamp connection valve
Clamp connection connects the pipe by using the clamp, which is easy to disassemble and maintain, and is widely used in food, pharmaceutical, و سایر صنایع.
Generally suitable for low to moderate pressure (up to 10 MPa)

The suitable connection method can be selected according to the required sealing pressure level.
1.4 Valve Opening Method
Valve installation and opening methods are divided into: manual valve, electric valve, pneumatic valve, hydraulic valve.
- Manual valve is the most used valve at present, the common manual valve has a handle type and a wheel handwheel type. Suitable for most piping systems.
- Electric valves are suitable for automated control systems such as HVAC, chemical production lines, and valve scenarios requiring remote control
- Pneumatic valves are suitable for factory assembly lines, robot arms, gas conveying and spraying equipment
- Hydraulic valve is suitable for heavy machinery and engineering equipment in chemical, Marine, and aerospace industries

2. The Performance Parameters of the Valve
- Valve pressure grade: PN (nominal pressure, such as PN16), Class (US standard, such as Class 150).
Indicator: Maximum working pressure (به عنوان مثال. PN16=16 bar).
- Valve operating temperature range: -50°C~200°C (conventional), -196°C~800°C (special working conditions).
Index: Temperature resistance of sealing material (such as EPDM ≤120°C).
- Valve flow coefficient: Cv/Kv value.
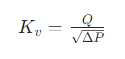

- Leakage grade: ANSI Class IV/V/VI, ISO 5208 A/B/C/D.
Indicator: Allowable leakage (such as Class VI ≤0.1 mL/min). - 5.Opening and closing torque: manual valve ≤50 N·m, electric valve ≤500 N·m.
Indicator: Drive matching.
3. Valve Material Parameters
1. Valve material
- Body material: برنجی, bronze, lead-free copper, RDA, Carbon steel (WCB), stainless steel (304/316)
به عنوان مثال, DZR anti-dezincification brass is a kind of corrosion resistant material, in which the zinc content is an important indicator. - Stem material:
- The ball material of the ball valve
- Sealing material: PTFE, EPDM, NBR, metal hard seal.
- Nut material

2. Valve surface treatment: nickel plating, epoxy coating, spray.
Test methods include: ASTM B117 salt spray test ≥48 hours, paint film impact resistance test, color paint and varnish grid test.
4. Valve Installation parameters
1. Valve installation direction: horizontal, vertical, incline.
به عنوان مثال, check valves are installed vertically, and conventional valves are installed horizontally.

2. Installation space requirements:
pipe spacing and installation position restrictions also have requirements for the size and shape of the valve

3. Maintenance space requirements:
Reserve the active space of the hand wheel/handle, the active space of the installation and removal tools, and plan the size of the access port.

5. Certification and Standards
1. Product certification:
ISO (بین المللی), CE/PED (EU), WRAS(UK), WaterMark (Australia), CRN (کانادا), API 6D (Pipeline valve), IAPMO (انجمن بین المللی مقامات لوله کشی و مکانیک).
به عنوان مثال, the United States, کانادا, and Australia have the most stringent requirements for lead-free valves.

2. Test standards
آ. API standards
API 598: Standard for testing tightness of valves.
API 600: Design and test standard for gate valves.
API 607: Standard for fire test of valves.
ب. ASME standards
ASME B16.34: Standard for the design, manufacture and testing of valves.
ASME B31.3: Standard for the design of chemical pipelines, relating to the application of valves.
ج. ISO standards
ISO 5208: Standard for testing the tightness of valves.
ISO 10497: Standard for fire test of valves.
ISO 9001: Quality management system standard for valve manufacturers.
d. EN standard
در 12266: Standard for testing the tightness of valves for the European market.
در 161: Performance standard for valves for gas applications.
e. JIS standard
JIS B 2002: Japanese industry standard relating to the testing and performance of valves.

3. Document requirements
Parameters: Material Certificate (MTC), inspection report (COC), drawing.
به عنوان مثال: نحوه تأیید گواهی WRAS برای دریچه ها?
6. Special Working Condition Parameters
1. Low temperature valve (Antifreeze Valve/Frost Proof Valve)
In cold areas, antifreeze valves are required. By detecting the ambient temperature, when the temperature is lower than 3 درجه, the liquid in the pipeline will automatically be discharged to prevent the pipeline from freezing and cracking
Specifications: BS 6364 (low temperature valve standard).

2. High pressure valve
Valve body thickness is the key parameter for valve pressure (به عنوان مثال. DN50 Class 600≈20 mm).
Specification: Comply with ASME B16.34 (high pressure valve design).
3. Sanitary valves
Sanitary valves are used in pharmaceutical and food production processes, using 304 و 316 stainless steel.
Indicators: Comply with 3-A Sanitary Standards.
7. Valve Procurement Cost Analysis
1. Procurement cost:
unit price, MOQ (minimum order quantity), payment method (LC/TT), transportation costs determine the direct procurement cost of the valve.
2. Operating costs:
service life, quality assurance years, installation difficulty, maintenance frequency, نگهدار, replacement costs, and inventory costs comprise the operating costs of valves.
3. Supply chain risk:
It is necessary to clarify the supplier’s delivery cycle (conventional 6-12 weeks, expedited 4-6 weeks) and mode of transportation, and stipulate the supplier’s default terms and amount.
8. Sustainability Requirements
1. Environmental compliance
- Parameters: RoHS/REACH (Restriction of Hazardous substances), energy efficiency level.
- استاندارد: ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System).
2. Low-carbon design
- Parameters: Material recovery rate (≥90%), lightweight (15% weight reduction compared with traditional design).

9. Supplier Evaluation
- Technical capabilities: investigate the supplier’s OEM/ODM customized design capabilities, non-standard valve processing experience, patent certificates, certification certificates.
- Production capacity: Evaluate the production capacity (daily output, monthly output) and existing orders through the size of the plant, the number of equipment, and the number of workers, and evaluate whether your orders can be delivered in time if you cooperate.
- Quality control capability: What quality inspection equipment does the supplier have (pressure testing instrument, flow testing instrument, leak detector, ultrasonic flaw detector).
- Case study: Investigate whether suppliers have executed orders for similar products of similar size. If you have no experience, you need to pay more attention in cooperation to ensure that every detail of the order product requirements is understood by both parties.
- After-sales service ability: Product warranty period (usually 2-5 سال ها) Quality suppliers can guarantee products for 10 سال ها.
- Packaging requirements: Whether the product packaging meets the requirements of long-distance transportation, such as shipping boxes and pallets
- Sample testing: needs to confirm whether the samples provided by the supplier meet the requirements of material, size, pressure, appearance, etc. Continue to communicate with the supplier if any adjustments need to be made after testing
Supplier evaluation form
In the early supplier evaluation, you can score suppliers, sort more suppliers of the same type, and select the best suppliers.
| Factor | weight | Key indicator | acceptance threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical adaptation | 30% | Cv/Kv value error ≤5% | in line with PID design requirements |
| Quality Compliance | 25% | Leakage level ≤Class VI | API 598 test passed |
| Total Cost of ownership | 20% | TCO below budget 10% | 5 year life cycle cost analysis |
| Supplier reliability | 15% | OTD ≥95% | Audit of historical delivery data |
| Sustainability | 10% | Carbon footprint reduction ≥20% | LCA report |
Tender project or multiple supplier quotation evaluation
When placing an order in the later period, when facing several high-quality suppliers, it is difficult to choose, you can also quantitatively evaluate the ability of suppliers according to different indicators, and calculate the most suitable valve suppliers for you.
| Scoring item | Supplier A | Supplier B | Supplier C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | 8 | 5 | 7 |
| Warranty | 10 | 6 | 6 |
| Delivery | 5 | 10 | 8 |
| Payment Method | 5 | 8 | 7 |
| Total Score | 28 | 29 | 28 |
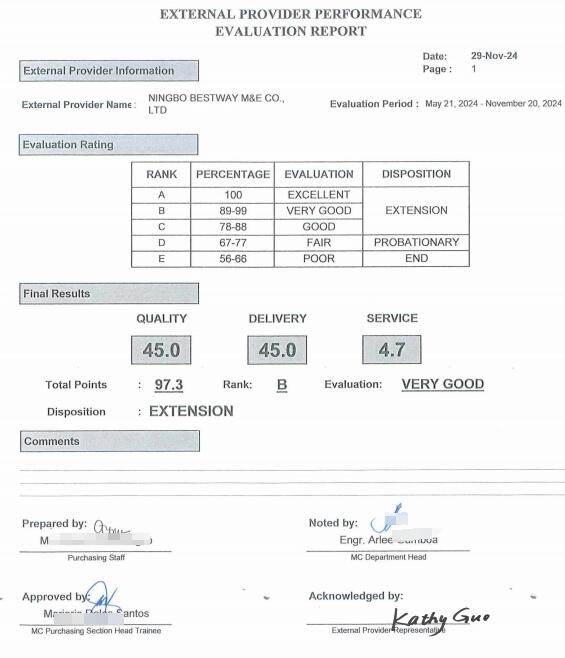
This is a rating sheet for BMAG from our clients.
The above is all the information that a professional valve procurement should know.
In strict accordance with the above content, the execution of the evaluation item by item can completely help a newly entered procurement specialist to upgrade into a procurement expert.
BMAG as a trusted partner with 20 years of experience in high-quality valve manufacturing, is committed to delivering excellence.









